When you are sneezing all the time, have a fever-like feeling, or can hardly breathe, it is quite natural to ask yourself the question: Am I having bronchitis or pneumonia? Both conditions hit your lungs, but the difference between bronchitis and pneumonia is more severe than most people are aware of. One of them is usually mild and temporary, whereas the other may be life-threatening unless one gets treatment sooner.
How do you tell if it’s bronchitis or pneumonia?
The simplest way to differentiate is by looking at where the infection sits in your lungs.
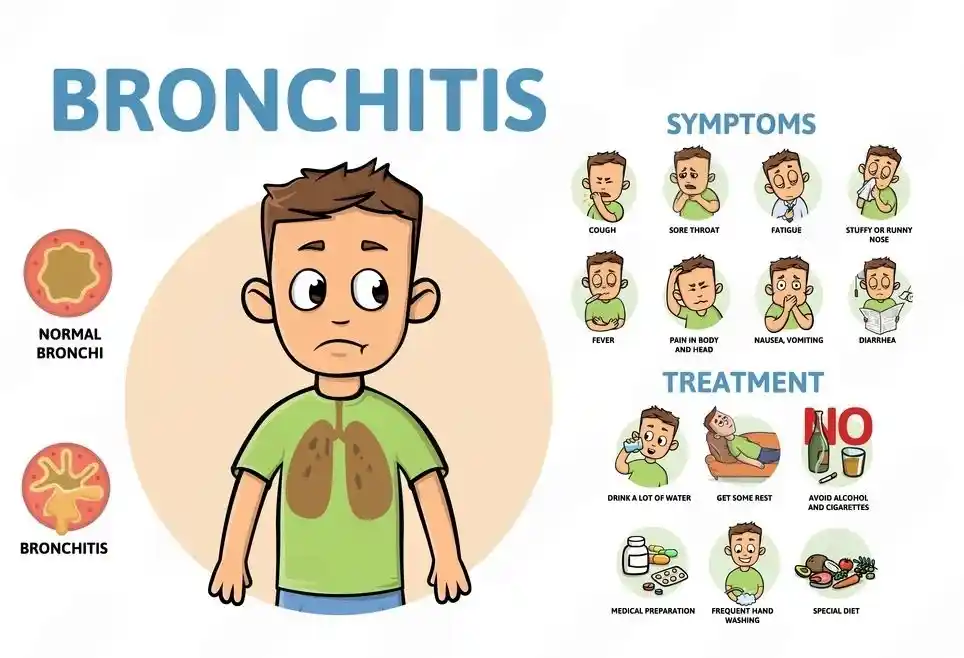
- Bronchitis is an illness that affects the bronchial tubes, which are the airways that move air to your lungs. It is normally viral and it is usually acquired after an episode of cold or flu vs pneumonia.
- Pneumonia attacks the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs, clogging them with fluid or pus and hence making breathing challenging.
So how do you know which one you have? You look at the bronchitis vs pneumonia symptoms.
Symptom Differences
| Symptom | Bronchitis | Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|
| Cough | Persistent, often with mucus | Wet or dry cough with thick or rust-colored mucus |
| Fever | Mild or none | High fever, often above 101°F (38.3°C) |
| Chest pain | Burning or irritation while coughing | Sharp pain when breathing deeply |
| Fatigue | Moderate | Severe exhaustion |
| Shortness of breath | Mild to moderate | Noticeably difficult breathing, even at rest |
| Chills/Sweating | Rare | Very common |
| Crackling sounds in the lungs | Rare | Often heard with a stethoscope |
The misunderstanding is between walking pneumonia and bronchitis. The walking pneumonia is merely a less severe version of pneumonia; you can still wor,k but you feel unusually fatigued, develop a persistent cough, and experience shortness of breath.
Treatment Differences
- Bronchitis: Treatments such as rest, hydration, cough suppressants, and inhalers are commonly prescribed for bronchitis, with the exception of cases where wheezing is present. The majority of the cases are viral and therefore, antibiotics are not typically required.
- Pneumonia: Particularly bacterial pneumonia requires prescription of antibiotics, steroids or even hospitalization in extreme situations.
When in doubt, pneumonia vs bronchitis should always be confirmed with a chest X-ray or medical evaluation.
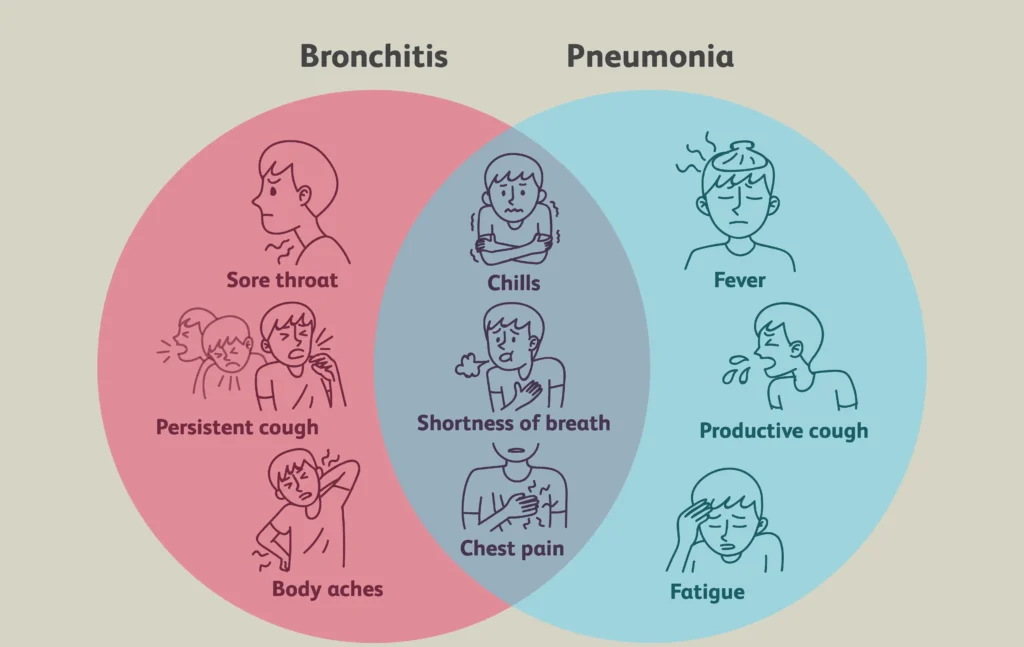
What Causes Bronchitis And Pneumonia
Knowing the causes of Bronchitis vs. pneumonia could enable you to know the risks at the early stages and prevent the diseases before they get out of hand. Even though both conditions impact the respiratory system, there is a difference in the triggers.
Causes of Bronchitis
Most cases of bronchitis begin with an infection, but bronchitis typically starts in the upper airways. The most common causes include:
- Viral infections: Viral bronchitis occurred following a flu vs pneumonia scenario, whereby the bronchial tubes are irritated by a simple cold or influenza.
- Smoking or Secondhand Smoke: Smoking damages the bronchial lining, making it more susceptible to inflammation.
- Air Pollution or Chemical Exposure: Dust, fumes, and industrial pollutants can inflame the air passages, especially in urban or occupational environments.
- Allergies or Asthma: Individuals with already acquired respiratory problems have a higher risk of bronchial irritation.
There are two main types: acute bronchitis, which is short-term and usually viral, and chronic bronchitis, which is long-term and often linked to smoking or COPD.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is worse as it attacks the air sacs in the lungs, thus blocking oxygenation. The major causes include:
- Bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common cause, and it mostly causes a mild case of bronchitis or pneumonia to develop into a more serious case of lung infection.
- Viruses: Viral pneumonia may be caused by the same viruses that cause bronchitis or flu, as compared to pneumonia (such as influenza or COVID-19).
- Fungi or Aspiration: On unusual occasions, inhalation of food particles, acid in the stomach, or mould spores may result in pneumonia particularly in individuals whose immunity is weak.
The key difference between bronchitis and pneumonia comes down to inflammation vs infection depth. Bronchitis affects the airways, while pneumonia fills the lungs with fluid, making it far more dangerous.
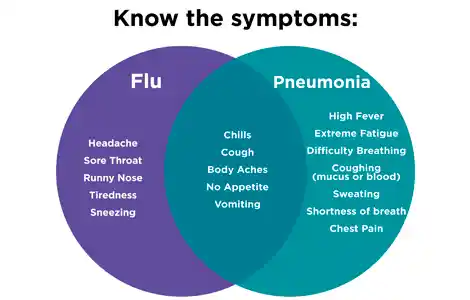
Common signs of both bronchitis and pneumonia
Due to the overlapping of symptoms, pneumonia vs bronchitis can easily be mistaken at the initial stages. Nevertheless, it is always possible to notice similar symptoms to recognize when you are developing something more serious.
Common signs include:
- Persistent Cough: In both scenarios, there is constant coughing. In bronchitis, mucus is normally clear or yellow, whereas in pneumonia, mucus can be thick, green, or blood-streaked.
- Chest Discomfort or Tightness: Bronchitis results in irritation of the airways, whereas pneumonia can result in pains that are sharp pains when breathing deeply.
- Shortness of Breath: Mild with bronchitis, but significantly more pronounced with pneumonia, particularly on doing simple activities.
- Fatigue or Weakness: The two diseases can cause unusual tiredness, both in instances of walking pneumonia vs bronchitis, as the impacts take a long time to clear, even when one is doing normal activities.
- Body Aches or Mild Fever: Viral infections that lead to bronchitis can cause body soreness, while pneumonia is more likely to cause high fever and chills.
If symptoms escalate rapidly, especially with breathing difficulty, high fever, or chest pain, it may no longer be simple bronchitis. At that point, Bronchitis Vs Pneumonia isn’t just a comparison; it’s a decision to seek medical attention.
How Are Bronchitis And Pneumonia Treated?
Though the symptoms of Bronchitis Vs Pneumonia can be similar, these two conditions can be treated in very different ways since one of them can be mild and self-resolving, whereas the other can become critical when not considered seriously. The primary objective in both scenarios is to lower inflammation, clear infection, and promote normal breathing; however, the strategy varies based on the nature of the condition, be it viral or bacterial, and the severity.
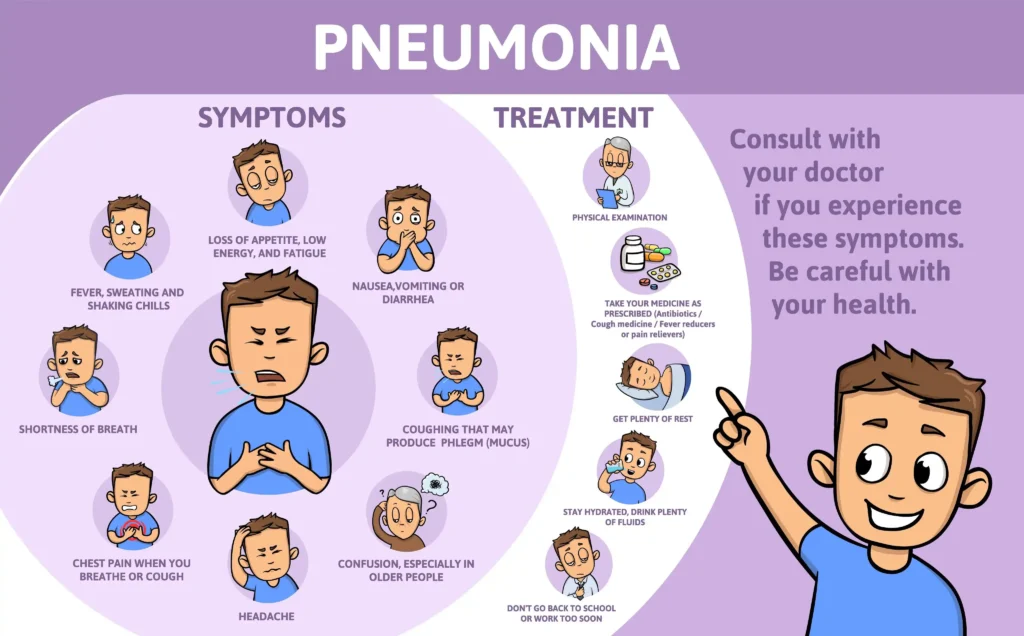
Treatment for Bronchitis
Most bronchitis cases are viral, which means antibiotics are usually unnecessary. Instead, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and helping the airways heal.
Common treatments include:
- Rest and Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus and clear the airways.
- Cough Suppressants or Expectorants: Expectorants help expel mucus in wet coughs, while suppressants are useful for dry, irritating coughs.
- Steam Inhalation or Humidifiers: Moist air soothes inflamed bronchial tubes.
- Inhalers or Bronchodilators: For those experiencing wheezing or tightness, especially people with asthma or chronic conditions.
- Avoiding Irritants: Smoke, dust, and strong fumes worsen inflammation, so staying in clean air environments is essential.
If bronchitis is caused by bacterial infection or starts progressing into bronchitis or pneumonia, doctors may prescribe antibiotics.
Treatment for Pneumonia
Pneumonia requires more aggressive treatment because it affects the deeper parts of the lungs. Understanding pneumonia vs bronchitis is crucial here: pneumonia can quickly become life-threatening if ignored.
Treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: Prescribed for bacterial pneumonia. It’s important to complete the full course, even if symptoms improve early.
- Antiviral Medications: Used in virus-related cases such as influenza or COVID-linked pneumonia.
- Steroids: Help reduce lung inflammation in severe cases.
- Oxygen Therapy: For patients struggling to maintain oxygen levels.
- Hospitalization: Necessary for elderly individuals, children, or anyone experiencing severe breathing difficulty or high fever.
Those with walking pneumonia vs bronchitis may only need rest, fluids, and oral medication. However, untreated pneumonia can escalate quickly, especially in people with weak immune systems.
Why Is Pneumonia Considered Dangerous?
Pneumonia is considered to be much more serious than bronchitis as it directly influences the capacity of the lungs to provide the blood with oxygen. Fluid or pus gets into the air sacs in the lungs, and then it becomes hard to breathe in and out oxygen, and even breathing normally becomes tiresome. The absence of oxygen may overstrain the heart and the brain and other important organs, particularly in the elderly, infants, or those with weak immune systems.
As compared to bronchitis, which simply irritates the airways, pneumonia may develop rapidly and cause complications like respiratory failure, sepsis, and death when left unattended. This is the reason why it is very important to identify the signs of bronchitis or pneumonia as quickly as possible.
Does bronchitis turn into pneumonia?
Yes, in some cases, bronchitis may become pneumonia, particularly in cases of no treatment and in cases of a weakened immune system. What may be a minor cough that is caused by the flu vs pneumonia will gradually deteriorate, progressing further to the lungs.
When the mucus is not properly cleared in the bronchial tubes, it accumulates, and the bacteria may multiply and enter the lung tissues, causing pneumonia. Bronchitis or pneumonia are liable to develop into something serious in people who smoke, those with asthma, COPD, diabetes, or chronic illnesses.
How Can I Protect At Home?
Prevention of Bronchitis Vs Pneumonia begins with the enhancement of your lungs and exposure to infection. The best preventive steps to take are to keep up to date on flu and pneumonia vaccines, particularly in the elderly, children, and people with chronic conditions.
It is also necessary to keep the indoor air quality good, and in the case of dry seasons, the humidifier may be used to help prevent the respiratory system from drying up and being exposed to irritation. Not smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke is a sure way to keep inflammation of the lungs to a minimum and make your natural defense system stronger.
When to reach out for help
Immediately contact a healthcare provider if you notice:
- Persistent high fever over 101°F (38.3°C)
- Chest pain while breathing
- Fast breathing or shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood or dark mucus
- Extreme fatigue or confusion
Never ignore severe bronchitis vs pneumonia symptoms. Early diagnosis makes treatment faster and recovery easier.
Final Thoughts
Understanding Bronchitis Vs Pneumonia can save you from unnecessary fear or even medical emergencies. While bronchitis is usually uncomfortable yet manageable, pneumonia is more aggressive and often requires proper treatment.
When your respiratory symptoms linger longer than expected, worsen suddenly, or impact breathing, don’t guess. Your lungs are too important to take lightly. Stay alert. Stay protected. And when in doubt, ask your doctor.